PepMap software allows gene localization through mapping of PSTs on raw genomic data (i.e. complete unannotated chromosomes).
As for protein identification, PepMap algorithm involves two steps:
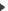 A mapping phase of PSTs on the six translation frames of genomic sequences allows putative localization of PSTs coding regions. By taking into account partial matches (i.e. one of the flanking masses of a PST is not recognized while the other is), PepMap may additionally provide important information about intron/exon boundaries. A mapping phase of PSTs on the six translation frames of genomic sequences allows putative localization of PSTs coding regions. By taking into account partial matches (i.e. one of the flanking masses of a PST is not recognized while the other is), PepMap may additionally provide important information about intron/exon boundaries.
 PST matching types PST matching types |
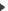 Then a clustering phase aims at grouping the PSTs matches belonging to the same protein in order to help identifying the corresponding gene. We devised several algorithms to this purpose but good results are obtained by simple single linkage clustering procedure: a match is clustered with other surrounding matches, if they are closer than a given maximum distance (typically 5000bp for Arabidopsis thaliana genome and 15000bp for human genome). Then a clustering phase aims at grouping the PSTs matches belonging to the same protein in order to help identifying the corresponding gene. We devised several algorithms to this purpose but good results are obtained by simple single linkage clustering procedure: a match is clustered with other surrounding matches, if they are closer than a given maximum distance (typically 5000bp for Arabidopsis thaliana genome and 15000bp for human genome).
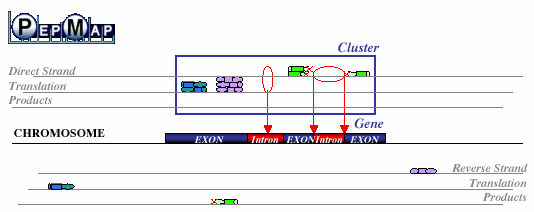 PepMap Gene localization PepMap Gene localization | |